Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed type of cancer. The three most common malignant skin cancers are basal cell cancer, squamous cell cancer, and melanoma, each of which is named after the type of skin cell from which it arises.
Skin cancer can be effectively treated by using specialized plastic surgical techniques to completely remove the cancerous tissue with preservation or restoration of aesthetic and functional unit of the involved anatomical region. The selection of an appropriate surgical technique is determined by the size and location of the tumour, involvement of adjacent structure, patient’s general condition and surgeon’s preference. These specialized plastic surgical techniques may range from a simple surgical excision to complex reconstructive surgical procedures combining with other medical specialities.
PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION
Communication is vital in order to achieve the patient’s goals. During the initial consultation, patients will have the opportunity to discuss with the plastic surgeon. The plastic surgeon will work closely with the patients to reach an agreement about the expectations from the surgical procedures involved and their long term benefits. Every patient is different, therefore a specific treatment regimen is planned to suit an individual’s need. The preoperative evaluation includes:
- Discussion type of skin cancer
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and previous medical or surgical treatment
- Use of current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drugs
- Discussion on anaesthesia and its risks
- Discussion on the likely outcomes of the treatment and any risks or potential complications
- Physical examination
- Local examination of the cancerous tissue including detailed assessments of the size, shape, location, surrounding structures and lymph nodes
- Photography for preoperative and postoperative evaluation
PREPARATION
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed type of cancer. The three most common malignant skin cancers are basal cell cancer, squamous cell cancer, and melanoma, each of which is named after the type of skin cell from which it arises.
Skin cancer can be effectively treated by using specialized plastic surgical techniques to completely remove the cancerous tissue with preservation or restoration of aesthetic and functional unit of the involved anatomical region. The selection of an appropriate surgical technique is determined by the size and location of the tumour, involvement of adjacent structure, patient’s general condition and surgeon’s preference. These specialized plastic surgical techniques may range from a simple surgical excision to complex reconstructive surgical procedures combining with other medical specialities.
PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION
Communication is vital in order to achieve the patient’s goals. During the initial consultation, patients will have the opportunity to discuss with the plastic surgeon. The plastic surgeon will work closely with the patients to reach an agreement about the expectations from the surgical procedures involved and their long term benefits. Every patient is different, therefore a specific treatment regimen is planned to suit an individual’s need. The preoperative evaluation includes:
- Discussion type of skin cancer
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and previous medical or surgical treatment
- Use of current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drugs
- Discussion on anaesthesia and its risks
- Discussion on the likely outcomes of the treatment and any risks or potential complications
- Physical examination
- Local examination of the cancerous tissue including detailed assessments of the size, shape, location, surrounding structures and lymph nodes
- Photography for preoperative and postoperative evaluation
PREPARATION
- Get laboratory testing or a medical evaluation
- Evaluation of general health status and any pre-existing health conditions or risk factors
- Adjust medications if for certain medical conditions
- Stop smoking and alcohol well in advance of the scheduled date for surgery
- Avoid taking aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs and herbal supplements before surgery
- Special instructions will be given on the day before and after surgery
RISKS AND SAFETY
The decision to have skin cancer surgery is extremely personal. Patients have to consider if the benefits will achieve their goals and if the risks and potential complications are acceptable. Therefore, it is important for patients to understand that every surgical procedure has its own complications and down time. However, if a patient is assessed properly before the surgery and postoperative care is given adequately, these risks can be eliminated or reduced.
Some of the common risks of skin cancer surgery:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Poor wound healing
- Wound breakdown
- Recurrence of skin cancer
- Systemic spread of skin cancer
- Skin discoloration
- Skin contour irregularities
- Skin sensitivity
- Swelling due to blood clot or fluid accumulation
- Injury to deeper structures such as nerves, blood vessels or muscles
- Possibility of revision or staged surgery
- Anaesthesia risks

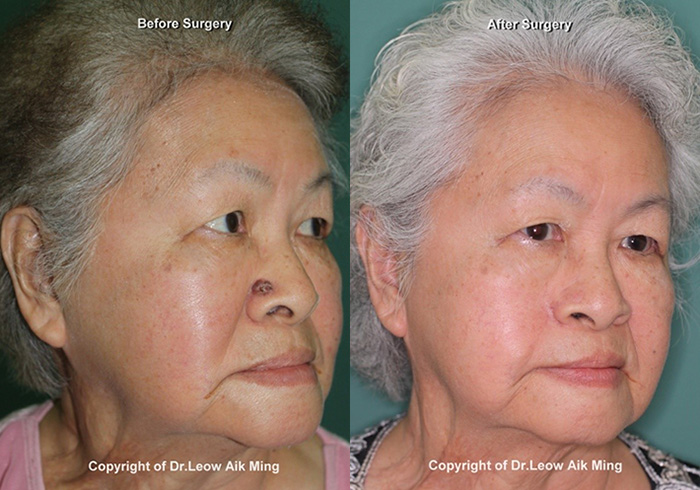
POST-OPERATIVE EXPECTATIONS
Postoperative expectations following skin cancer surgery may vary depending upon the invasiveness of the procedure. Simple skin cancer surgical procedures can be done on an out-patient basis. These procedures have shorter recovery time and patients may resume their routine activities with 3 -5 days after the procedures. On the other hand, skin cancer surgery that requires extensive reconstructive procedures may need a longer recovery period. The initial healing phase for skin cancer surgery may include localized swelling, discoloration or discomfort and this may take 1 to 2 weeks. Sutures will usually be removed about 7-10 days after the surgery. After that, the healing process will continue for several weeks to months for the scar to fully restore and fade. A patient should be aware that skin cancer can recur after surgery. Therefore, after skin cancer surgery, a patient should follow up regularly. It is also important for the patient to be educated about the risk of cancer recurrence and to perform self-examinations for any parts of the body to look for suspicious lesions.
POST-OPERATIVE CARE
- Regular application of prescribed ointment and cleaning the surgical wound as instructed
- Avoid excessive sun exposure during the healing phase
- Regular use of moisturizer and sun screen on the scar area
- Application of topical scar gel and massage around the scar area will improve the appearance and texture of the scar
– COPYRIGHT OF DR LEOW AIK MING
